A Dermatologist's Guide for Defying Skin Ageing
Because taking care of your skin is a form of self love (7 min read) - Issue #84
Proper skincare is not just about maintaining a youthful appearance or achieving flawless beauty; it is essential for overall health and well-being. The skin, being the largest organ of the body, serves as a protective barrier against external elements and plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy internal environment. Here are a few reasons why skincare is of utmost importance for our health.
Firstly, skincare helps to protect our skin from harmful environmental factors. The skin is exposed to pollutants, UV radiation, and harsh weather conditions on a daily basis. Neglecting skincare can lead to various skin problems, such as sunburns, premature aging, dryness, and even skin cancer. Regular use of sunscreen, moisturizers, and protective clothing can help shield the skin from these damaging factors, reducing the risk of skin diseases.
Secondly, a good skincare routine promotes proper hygiene. Our skin is constantly exposed to sweat, dirt, and bacteria, which can clog pores and lead to acne breakouts, infections, and other skin conditions. Cleansing the skin regularly helps to remove impurities, excess oil, and dead skin cells, allowing the skin to breathe and function optimally.
Moreover, skincare plays a vital role in maintaining the skin's natural balance and moisture levels. Dry, dehydrated skin is more prone to irritation, inflammation, and infections. Moisturizers and hydrating products help to nourish and replenish the skin, keeping it supple, soft, and resilient. Additionally, skincare products containing antioxidants and vitamins can provide protection against free radicals, which can damage skin cells and accelerate the aging process.
Lastly, skincare can have a positive impact on our mental well-being. Taking care of our skin is a form of self-care and can contribute to increased self-esteem and confidence. When our skin looks and feels healthy, it can boost our overall mood and reduce stress levels.
This is the second part of my conversation with Dr Divya Sharma. The first part can be read in Issue 74 of the newsletter.
Ageing of the skin is inevitable but premature ageing is preventable. It is a continuously evolving subject as different skins follow different trajectory. Gradual loss of skin elasticity leads to the phenomenon of sagging. The rate at which dead skin cells shed decreases in ageing skin and hence dead skin tends to accumulate giving dullness to skin. This is an important fact as this becomes a target of anti ageing strategies to accelerate cell turnover. There is a marked loss of collagen and reversal of ratios of collagen 3 and collagen 1 content. The overall collagen content per unit area of the skin surface is known to decline approximately 1% every year. Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are among the primary skin constituents in the dermal layer which helps in binding water. In photo-aged skin, GAGs may be associated with abnormal elastotic material and thus be unable to function effectively. There is also a decrease in Hyaluronic Acid in the upper layers of skin and decline in function of dermal levels.
There are some inevitable structural changes to the skin associated with the gravity impact, muscles action, loss of volume, diminishing and redistribution of superficial and deep fat, loss of bony skeleton support which all together lead to the face sagging, changes in shape and contour.
Tools for prevention of Skin Ageing
Preserve epidermal barrier - Skin is the largest functioning barrier of the body. It prevents the entry of infectious organisms , allergens , and pollutants into the body. Skin hydration is the first step to younger looking skin. One must use non comedogenic moisturiser to enhance the barrier and to compensate for the loss of natural hydration of the upper layers of skin.
Prevent loss of the collagen and elastin - Sunscreen is the most effective remedy for prevention of degradation of collagen and elastin. It performs a passive function of preventing exposure of skin to UV light which leads to deposit of elastotic material into dermis.
Prevent or reduce inflammation of skin - Free radicals induce damage in skin at all levels. The body is in a constant fight against these free radicals to prevent degradation of the dermal components and ageing.
Tools to effectively defy ageing
Sunscreens - Sunscreens are the products combining several ingredients which protect the skin by absorbing, blocking or scattering UV radiation. Two types of agents protect the skin from sunlight, one which reflects the UV rays and the other which absorbs the UV rays. Reflectors (physical sunscreens) are the substances which when present on the surface of the skin reflects the UV rays thus preventing them from entering the skin. Absorbers (chemical sunscreens) absorb the sunlight, and they are active against a specific spectrum of sunlight. So these can be used individually or in combination to act as a sunscreen. The sunscreen with a minimum sun protection factor of 30 (SPF 30) should be used to obtain the maximum benefit.
Cell cycle regulators - Cell cycle regulators, such as vitamin A derivatives, polypeptides and botanicals, act directly on the collagen metabolism and stimulate the production of collagen and elastic fibres. This is a strategy to reduce the breakdown of collagen and enhance its growth to defy ageing.
Retinoids - Vitamin A (retinol) and its derivatives (retinaldehyde and tretinoin) are also a group of agents which are perhaps the most popular on social media. They induce the biosynthesis of collagen to some extent and reduce the expression of MMP 1 or collagenase which degrades collagen at a fast rate. Retinol is the substance that is most often used as an anti-ageing compound and, compared with tretinoin, causes less skin irritation. Retinol works not only on extrinsic but also on intrinsic skin ageing and boosts collagen metabolism. Very sensitive and dry skin may get irritation or in severe cases retinoid dermatitis. Bakuchiol is derived from seeds of Psoralea corylifolia and has shown to have similar activity like Retinol.
Peptides - The role of peptides in cosmeceuticals is based upon the fact that peptide fragments of collagen and elastin can act as positive feedback signals for their own continued synthesis. Matrixyl , Argireline and Cu - GHK are few popular names in this segment.
Antioxidants - Vitamin C is perhaps the labelled holy grail ingredient of skin care on social Media. A lot is talked about the efficacy of Vitamin C in skincare but the penetration of vitamin C remains debatable. When plasma levels are low, some Vitamin C can be delivered to the epidermal layer by topical application, although the efficacy of this is highly dependent on the formulation of the cream or serum used on the skin. Vitamin C, as a water-soluble and charged molecule, is repelled by the physical barrier of the terminally differentiated epidermal cells. It is only when pH levels are below 4 and vitamin C is present as ascorbic acid that some penetration occurs but whether this results in increased levels in the metabolically compromised Stratum Corneum is unknown. Blindly trusting that all formulations will achieve the same result is debatable. One must also understand that very sensitive skin especially with compromised skin barrier may not tolerate Vitamin C preparations.
Niacinamide - Niacinamide’s role as a key player in antioxidizing reactions has been the focus of most of the studies. Niacinamide has been shown to improve skin barrier by increasing lipids and epidermal protein.This action leaves skin more resistant to irritation and decreases water loss from skin. Niacinamide also reduces pigmentation by a mechanism that inhibits melanosome transfer from melanocytes to keratinocytes. It cannot certainly be a treatment modality as it is a weak molecule but can be a useful add on in people especially with sensitive ir dry skin.
Hyaluronic acid - Hyaluronic acid helps in preservation of hydration and elasticity of the skin. Topical creams or serums are less effective than micro injections into the dermis known as skin boosters. Ageing skin is not able to retain moisture and hence this molecule may help in hydration and even reduce pigmentation to certain extent. Intradermal injection of hyaluronic acid known as skin boosters are useful in improving the skin texture and hydration.
Alpha hydroxy acids - They work by removing or decreasing dead skin and restores the epidermis and hence preventing fine lines and wrinkles. Furthermore, application of hydroxyacids causes dermal thickening by stimulating biosynthesis of glycosaminoglycans, collagen, and elastic fibres, improving wrinkles and fine lines
Do you know?
Even at its thickest point, our skin is only a few millimetres thick. But it's still the body's largest and heaviest organ, making up about 1/7th of our body weight. Depending on your height and body mass, your skin weighs between 3.5 to 10 Kgs.
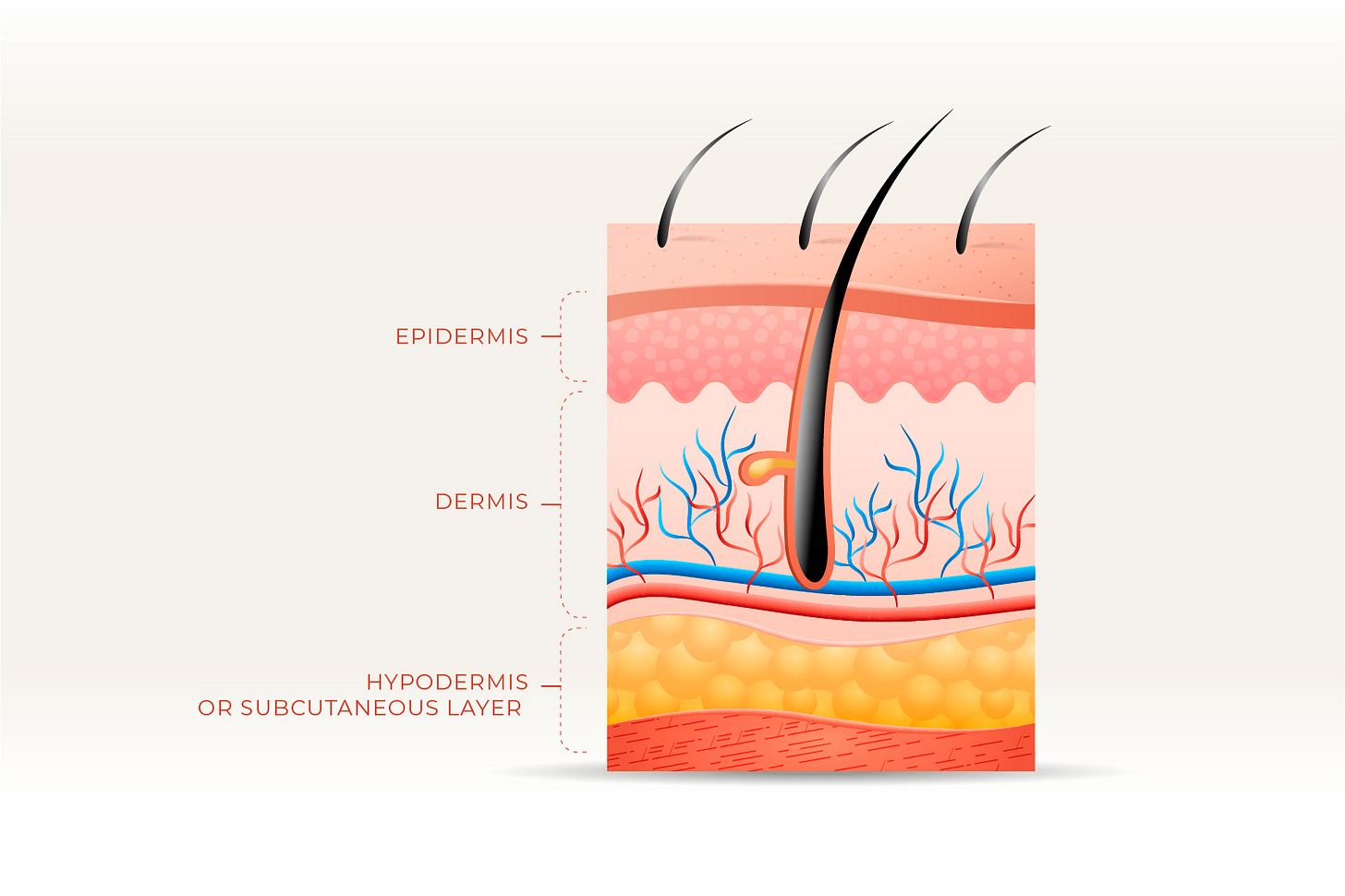
Our skin relies on the specialized structures in its three layers:
The ‘Epidermis’
The ‘Dermis’
The ‘Subcutaneous layer’ (sometimes called the ‘Hypodermis’, or ‘Fat layer’)
OUTERMOST LAYER
The Epidermis — the outermost layer of the skin— is a protective physical barrier, about as thick as a piece of paper. As the older cells on the surface of the epidermis die and fall off or are rubbed off, younger cells from below rise to take their place. This continuous cycle completely renews the skin surface about once a month. The epidermis plays a key role in protecting you from the sun’s radiation and has a very vital role in immunity as well.
THE MIDDLE LAYER
The dermis lies directly beneath the epidermis. It is a thicker layer that contains collagen, blood and lymph vessels, nerves, hair follicles, and glands that produce sweat and oil.
Blood vessels in the dermis expand or contract to maintain a constant body temperature.
White blood cells patrol the dermis to fight infectious microbes that manage to break through the epidermis.
Cells called fibroblasts secrete collagen, which gives the skin its strength and firmness.
Elastin fibres made of protein in the dermis give skin its elasticity.
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a humectant — a substance that retains moisture — and it's capable of binding over one thousand times its weight in water.
THE DEEPEST LAYER
The Hypodermis, which consists of connective tissue and fat, lies between the dermis and underlying muscles or bones. It, too, contains blood vessels and infection-fighting white blood cells, but not to the same extent as in the dermis. Fat in the subcutaneous layer stores nutrients and insulates and cushions muscles and bones.
NAILS
Our nails are skin, too. They’re a thickened, hardened form of epidermis. Nail cells originate from the base of the nail bed. They die quickly, but unlike the keratinocytes, they aren’t sloughed off. Nails are like windows to inner health and reflect minutest changes inside the body. Anaemia and thyroid disorders can be merely detected on examining the nails.
All illustrations by Kratika Singhal
Dr Divya Sharma is a renowned Dermatologist and Trichologist based out of Bengaluru. She is on the scientific committee of various national, regional dermatology congresses and is often invited as faculty to the Indian Academy of Dermatologists, Venereologists and Leprologists (IADVL), Association of Cutaneous Surgeons of India (ACSICON) national conferences. A member of IADVL special interest group (SIG)- Aesthetics, she runs her own practice, Dr Divya's Skin and Hair solutions in Bengaluru and can be reached through her website www.drdivyasharma.com. You can connect with her on Twitter @divya_sharmaMD
In the next issues of Good Vibes, I will be covering about ‘How to eat smartly’ (for paid subscribers only) and ‘Shifting mindset from negativity to positivity’ (For all subscribers). Upgrade to paid subscription to read all previous issues.
Did you like this issue? If yes, consider dropping your ❤️ on the socials and sharing it with anyone who you think will benefit from it.
If you have feedback, I am all ears. You can DM me on my socials or drop me an email at me@sandeepmall.com
See you! Take care.





Very Informative!